The record industry in Malaysia first started in the late 50s in Singapore. In the 60s, record companies were setup in Kuala Lumpur. The years of 70s were the phenomenal growth period for the local record industry. The local labels had controlled the market with both original materials and cover versions.
In the late 70s and the early of 80s, the industry was facing serious piracy problem. At the same time, big multinational companies such as Columbia Broadcasting System (CBS), Warner Music with strong financial support entered the market with great international products and consequently controlled the market.
2.2 Competition
According
to the chairman of the Records Industry of Malaysia (RIM), Mr. Rick Loh
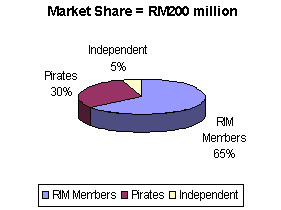
(1997), the market size of the industry is about RM200 million in 1997.
Out of this amount, 65% is shared by RIM members consist of 23 record companies.
Another 30% is controlled by pirated products and the rest of 5% is shared
by independent labels.

BMG, Sony Music, EMI, Warner Music, Polygram and Rock Record are the leaders in the local record industry. BMG is reported as the top company which once had a market share of 50%. Other followers are multinational companies such as Pony Canyon, Universal, Form, What’s and also local established companies such as New Southern Records, Suwah and Life Record.
Most of the record companies in this country sell not only their own labels, but also sell for the associated local and foreign labels. Since the international companies controlled most of the superstars’ repertoire over the world, they are always in a better position in the marketplace.
2.3 Product Format
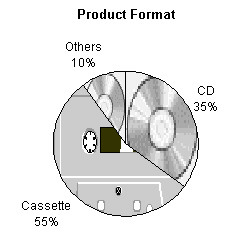
Other
existing formats include video cassette (VHS), video compact disc (VCD)
and laser disc (LD). They are the main carriers for audiovisual products.
VCD has overcome VHS and LD as the most popular format for music video
(MTV). This is due to its economical price, digital technology quality
and the ease to use with personal computer. It has been introduced to the
local market in 1995 and has a broader distribution channel where it is
sold at most record stores and computer software centers.
The latest formats for sound carrier are the mini disc (MD) and digital
versatile disc (DVD). MD player and diskettes where introduced in 1996.
Their rates of acceptance are still going slow in the markets. The new
DVD player and discs are most likely to reach the market in about two years.
The world leading record companies and consumer electronics manufacturers
have agreed on the broad technical guidelines for DVD audio format. DVD
is seen as a replacement for compact discs (Reuters 1997).
The
new DVD will have a capacity for an enormous amount of information. It
is able to store seven times more digital data than today's CDs. It may
serve as the carriers for audio, video and computer software and multimedia
releases. It also signals a fundamental shift in the record business, away
from two-channel stereo sound to multi-channel audio, using six speakers.
2.4 Market Segment
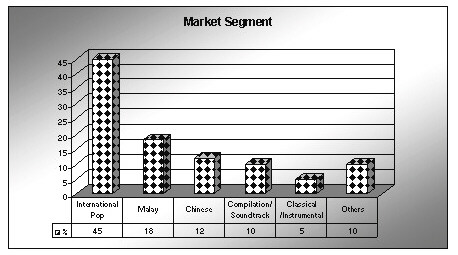
The main market segment for Malaysia’s record industry is the international
pop, which covers the popular international English albums, having a 45
% of the market share. Local Malay albums enjoy 18% share in the market,
and Chinese albums take 12% of the market share. Another important segment
is the compilation /soundtrack albums, which feature the most popular songs
or songs of movies, dominating the market with a 10% share. It is followed
by the segment of classical /instrumental /jazz with 5% of market share.
The rest of 10% is shared among other styles such as Japanese, Indian,
oldies, children and gospel.
Nearly all the sales of records are derived from album selling. Single, a compact disc or cassette with only one or two songs is not popular in Malaysia. Recently, it is a new development in the market where imported singles are sold in small quantities at some record stores.
2.5 Price
The pricing method normally used in record industry is the cost orientated pricing. A percentage is added to the cost of the product (Pride 1995). The cost of record including recording production cost, royalties for composer and artist, the disc or cassette manufacturing cost and promotional costs.
Price competition is rare in the record industry of Malaysia. Generally, prices are different among product groups due to different rates of royalty payments among territories. The table shows the prices of different product groups:

Normally the retailers will sell these compact discs and cassette tapes below the suggested retail prices, but selling price is standard within every product group, subject to the competition among retailers within a particular area.
2.6 Distribution Channel
The common practice for distribution is the multilevel distribution, which functions with the participation of wholesalers and retailers. Mail order is not popular while television marketing and Internet marketing are still new to local consumers for records purchasing. There are three major types of retailers:
a) Retail Chain
These retailers have chains through out the country, such as Salem Power Station, Music Valley, CD Rama, Music Power House and Speedy. Salem Power Station has 8 outlets around Kuala Lumpur and Music Valley has more than 20 outlets within the states. Speedy is an associated retailer of Speedy Video, while CD Rama and Music Power House are the associated retailers of Popular Bookstore and MPH Bookstore respectively.
All of these retail chains practice central purchasing and most of them are located in shopping complex in major cites. Most of them have online connection with RIM which gives immediate information on their sales that determines the position of albums at RIM Charts.
b) Record Stores
These are the traditional retailers that sell records of various labels in their shop. They are located in cities and towns throughout the country. Most of them get the supplies through the wholesalers.
c) Night Market (Pasar Malam)
Pasar malam, another channel that contributes to the sales of recorded music albums. The markets sell most of the popular products and oldies, captures the other types of consumers who the majority of them are housewives, workers and villagers.
2.7 Industry Competitors
The record industry of Malaysia is facing competitions from pirated products, imported products and also foreign products sold through direct marketing. Pirated products give the most challenges where they share about 30% of the total market in 1997. The record industry competes with other kinds of entertainment as well.
a) Pirated Products
Since few decades ago, piracy was the main problem in this industry. Piracy was very serious in the early of 1980s. Pirated cassettes were sold openly at most of the record stores for one third of the original cassette’s price. At that time, pirated product occupied 70% of market share. After the Copyright Act (Act 322) was implemented in 1987, piracy became less serious. According to RIM, pirated product still dominates about 30% of the market with RM60 millions of annual sales.
b) Imported Product
There are retailers who import compact discs and cassettes directly from abroad. For example, Virgo Music of One Utama shopping center sells about 40 percents of imported product in their shop. There are some reasons to import. Firstly, none of the local company represents the products. Secondly, record companies do not manufacture these products locally due to its small quantities. This is significant especially for singles and also classical, jazz, world music albums. Thirdly, it is faster to get supplies by import. Normally, multinational companies will take some time in preparing to market their foreign products. Retailers who import will take a step further in retailing these new albums. Normally imported products are sold around 100%-120% of normal price. They are marketable due to their exclusiveness.
c) Direct Marketing
Direct marketing has been used to market recorded music since many years ago. Some local or foreign independent labels and retailers advertise in magazines and offer to sell their products by mail order. Local consumers order the classical albums especially from abroad where these albums are hard to find in local.
Today, direct marketing is developed into television marketing and Internet marketing. Internet marketing has created better opportunities for local consumers to buy products from abroad. Unlimited information and products from whole of the world can reach to the consumers. The industry may lose some of markets through the more exposures, choices and exclusiveness of world products.
d) Other Entertainment

The development in the other entertainment industries gives competition to the record industry. Today, there are 5 television stations in this country - RTM, TV3, Metro Vision, Mega TV and Astro. There are a total of more than 40 channels featured by these stations. The Mega TV is a cable television and the Astro broadcasts through satellite. Both of them are subscription based. These stations provide multi channels of interesting programs, giving both viewing and listening pleasures. Consumers’ subscription to the commercial stations affects the sales of recorded music albums.
Apart from the direct competitors, there are more new radio stations on air in this country since the last few years. There are 6 national channels and more than 10 state channels run by RTM, the national broadcaster. The other commercial radios included Rediffusion, Time Highway Radio (THR), RFM and the Astro radios, featuring Hitz FM, Mix FM, Classic Rock and Light & Easy. Radio broadcasts enable audiences enjoy free music which do not encourage the sale of music albums.
Other
entertainment such as home videos and movies also give competition to the
record industry.